《维多利亚2》的社会改革系统是一种机制,它模仿了维多利亚时代晚期和进步时期旨在治疗社会弊病的倡议浪潮。从历史上看,这些改革往往是在短时间内停止了许多年来的常态,而且主要由私人公民和企业来完成,几乎没有政府干预。这些改革也极为多样化,从20世纪初被普遍引用的安全或卫生法规,到19世纪末和20世纪初错误发动的禁酒运动。
如你所见,社会改革的历史事实相当混乱。为了简单起见,《维多利亚2》只显示了最常见的改革,倾向于更容易管理的国家改革,而忽略了私营部门的改革。总的来说,这些改革可能被视为有益或有害,这取决于个人的品味,但无论你对改革的看法如何,每一项改革都有一定的成本和收益。
改革类型与代价
《维多利亚2》有七种类型的国家社会改革可供选择,其中六种有五个不同的等级,一种有四个。每个改革都有不同的成本和收益,下面将详细说明。在这七项改革中,有五项增加了行政需求,因此纳入了行政预算,而其余两项(养老金和失业补贴)则由社会支出预算处理。任何由行政官僚机构进行的改革,每一级都会增加0.1%的官僚人口需求。例如,如果一个玩家要实施最高水平的最低工资改革,他的国家就会需要1.4%的官僚来实现100%的行政效率,而不是1%。改革可能还需要付出其他代价,而有些代价比其他代价更明显。例如,几次改革带来的工业效率下降可能会摧毁许多工厂,或要求工厂补贴。对于一个工业大国来说,工业补贴的成本会变得难以承受,所以改革者要小心了。
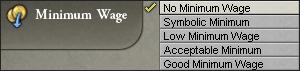
最低工资
最低工资改革是一个模棱两可的改革,因为它只会影响到那些拥有资本家的工厂。没有资本家的工厂会无视最低工资。如果有资本家存在,最低工资将作为雇工的最低收入。如果工厂利润除以2比最低工资高,那么不涉及最低工资问题。否则,少于最低工资的部分将首先从资本家的收入中提取,如果还不够的话,从利润中提取(即使这会使其变成亏损)。下面的折叠部分描述了该量的计算方法。
经验表明,实施最低工资会对工业产生毁灭性的影响,特别是如果实施改革的国家上任了一个自由放任的执政党,从而不能发放工业补贴的时候。这项改革由行政官僚处理,实施改革会增加行政开支及官僚人口的需求。
Calculation
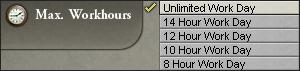
最大工时
最大工时,顾名思义,设定了最大工作时间的上限。从游戏机制的角度来看,它每一步减少贫穷阶层和中产阶层的奢侈品需求5%,最多减少20%。这使得实现奢侈品的满足明显更容易。如果你试图保持人口的幸福、寻求转换或同化人口或任何其他任务,从而需要高水平的人口满足度,这项改革会是一个有用的工具。
然而,每一步改革都会使工厂吞吐率降低5%,这会严重影响工业生产,进而影响盈利能力。自由放任主义者要再次当心当心,这项改革可能会使你的工厂陷入亏损,一夜之间摧毁大量的工业。如果实施了改革国家拥有大量的资本家、大量的职员、高工业商业科技水平、发达的铁路网,或者上述任何一种组合,那么这种代价就不那么强大了。这项改革由行政官僚机构处理;其费用在预算的该部分中计算,其实施增加了上述官僚机构的需要。 The cost, however, is a 5% decrease in factory throughput per step. This can seriously affect industrial production, and thus profitability. Again, Laissez-Faire beware, this reform could send your factories into the red, wiping out vast swathes of industry overnight. This cost is less potent if the reforming country has large populations of capitalists, large populations of clerks, high industrial and commercial technology levels, well-developed railway networks, or any combination of the above. This reform is handled by the administrative bureaucracy; its costs are calculated in that section of the budget, and its implementation increases bureaucratic needs as described above.
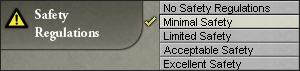
安全守则
This reform imposes a state-required safety regime on industrial enterprises. This decreases the everyday needs for all strata (rich, middle, and poor) by 5% per step, to a maximum of 20%. As with the maximum work hours reform, this benefit can seriously improve the situation for a country's pops, and in the process have a significant effects on the player's ability to accomplish his goals.
The costs of this reform are a 25% increase in factory maintenance per step, for a whopping 100% total if the maximum reform level is achieved. As with the other reforms, this can seriously affect the profitability and viability of industry of a country. Also as with other reforms, look to capitalists, clerks, technology, and infrastructure to abate these costs. This reform is handled by the administrative bureaucracy; its costs are calculated in that section of the budget, and its implementation increases bureaucratic needs as described above.
失业救济
The unemployment subsidies reform creates a state-monopolized unemployment insurance regime. As it does in reality, unemployment subsidies provide an income supplement to out-of-work pops. This subsidy can be very helpful to the player, though it may not appear so at first. Population promotion and demotion are affected by a variety of different variables, but the most significant variable that promotes pop demotion is needs fulfillment. If a pops needs go unfulfilled (usually because their income cannot support its strata's needs) it will eventually demote to a lower pop with fewer needs. In cases of capitalists, clerks, and craftsmen, this is an incredibly annoying reality, as it can seriously hamper the player's ability to maintain a consistent or growing population of industrial workers. Unemployment subsidies help to ease this problem and insure a stable base of skilled workers.
The costs of this reform are calculated as described below and are funding via the social spending budgetary category. As such, this may be one of the more attractive reforms to a player of industrial powers, as its costs are borne entirely by the state budget, not factory owners, and it actually can help preserve the most important factor of industrialization in Victoria 2: a large base of craftsmen (as well as capitalists and clerks).
Calculation
Administrative Efficiency (AE)
Social Spending (SS)
Life Needs price unadjusted by Consciousness (LN)
Effective Tax (ET)
Amount of unemployed POPs (X)
Social welfare income (Y)
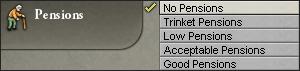
退休金
The pensions reform provides state-guaranteed old age pensions. All pops in game are basically representative of the working-age male population. This is why the pops, and consequently your "population" and the population of provinces, all added together equal 1/4 of your "total population." It is therefore assumed that each visible pop has a number of young, female, or old people attached to it. Thus, pensions increase your pops' incomes on this rationale. Pensions are a good way to increase your poor and middle pops' purchasing power, so long as you have the money to foot the social spending bill.
The costs of this reform are calculated through the social spending budgetary category, and is dependent upon your population size.
Pensions are calculated like unemployment subsidies, but for all POPs.
卫生保健
It is undoubtedly the most potent social reform, as it increases population growth by a 0.02% per level, to a maximum of 0.08%. Population growth is extremely desirable in Victoria 2, as industrialization relies almost exclusively on the conversion of excess farmers and laborers into craftsmen. The fastest way to acquire this desired excess is to increase your total population beyond the level needed to fully staff RGOs. Thus, this reform, especially if implemented relatively early in the game, is extremely important.
As if the benefits of this reform weren't impressive enough, it has no other costs aside from administrative ones. This reform is handled by the administrative bureaucracy; its costs are calculated in that section of the budget, and its implementation increases bureaucratic needs as described above.
公共教育
The public school reform creates a public school system that educates your nation's youth. This one is unique in that, unlike the other six social reforms, the public school system only has four levels. The first level of reform increases your education efficiency by 10%, equivalent to one level of social thought research in the culture section, while the other two increase it by a further 5% each. This reform is useful for any nation that wants to improve its literacy, especially newly civilized nations that need to quickly catch up on research. Generally, the player wants to enact this reform only if desperate for more literacy, as it isn't as immediately effective as health care or pensions are. This reform is paid for through the administrative budget, and increases your need for bureaucrats as described above.
实施和废除改革
Most countries begin with no social reforms. Some may have a single low level reform, but this is the exception not the rule. For a list of base social reforms indexed by country, see country social reforms. Like political reforms, a country can implement a social reform if its Upper House is in favor of doing so. Reforms must be implemented or repealed consecutively. That is, a player cannot simply jump from a low or nonexistent reform up to a high-level reform or vice versa, this must be done in steps. The exception to this rule is if the reform is imposed by event. There are several random events that give the player choice over the implementation or repeal of social reforms, as well as a number of country-specific events.
Certain ideologies are more likely to implement social reforms than others. Socialists and Communists are the most likely to vote in favor of social reform. Liberals may support reforms to a degree depending on circumstance. Conservatives and Reactionaries are unlikely to ever support reforms (unless militancy is very high), and if Reactionaries hold the Upper House, they can repeal social reforms. Immediately upon implementing a social reform, the Upper House becomes more Conservative, which may delay the implementation of further reforms if your Upper House does not adjust itself quickly.
If the player wishes to implement the social reforms as quickly as possible, it is advised to deliberately drive militancy up to make the uncooperative parts of Upper House vote "Yes". Militancy can be driven up by holding elections and then changing the ruling party, or through various events and event choices.
其他
The social reforms data can be accessed by locating the Paradox folder in the drive to which it is saved, the navigating to Victoria 2/common/issues.txt.